Herpes is quit common problem.
More than one out of every six people aged 14 to 49 years have genital herpes.
And the scariest fact is that Herpes in the eye is a leading cause of blindness in the world.
To protect yourself and your loved ones we have created this post so you could get to know what and who is Herpes!
About Herpes
Herpes is a long-term recurring skin infection, probably best known for the blisters and sores it causes.
It is caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV), which affects mucosal surfaces, anal region, external genitalia and skin in other body parts.
HSV infections either result in symptomatic disease at the point of viral entry (e.g. genital area or face) or asymptomatic one, which remain unrecognized.
Types of Herpes
Herpes are classified into two major types, based on the infected body parts.
- HSV-1, generally referred as oral herpes
- HSV-2, mostly known as genital herpes
HSV-1 (Oral Herpes)
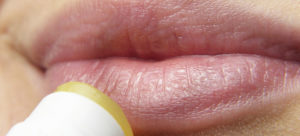
In oral herpes, the infected parts involve mouth or face.
Oral herpes may produce group of small blisters, mostly called fever blisters or cold sores.
Herpes Simplex 1 causes sores, fluid-filled blisters or ulcers anywhere inside mouth, including tongue and gums.
Oral herpes can be a cause of genital sores as well.
Chin, around the mouth and upper lip are the most common locations for HSV-1 infections, whereas they can cause sores around nostrils and inside nose too.
Eyes can also get affected by herpes.

Eye herpes, also known as ocular herpes, is typically a recurring viral infection, resulted due to herpes simplex virus (type 1).
It affects the eye by causing scarring of cornea and inflammation, sometimes called cold sore on eye.
The major features of eye herpes infection include tearing, swelling around eyes, foreign body sensation, irritation, redness of eye, eye sores, sensitivity to light and watery eye discharge.

HSV-2 (Genital Herpes)
Genital herpes is one of the known sexually transmitted diseases (STD).
These herpes can result in sores on thighs, buttocks, rectal area or genitals.
One can get this virus through oral, anal or vaginal sex with someone affected by it.
This virus is transmissible even in the absence of sores.
Though the herpes simplex virus (type 2) sores may occur on other body parts too, usually they exist below the waist area.
The below figures show what does genital herpes look like.

HOW HSV-1 Differs From HSV-2?
- HSV-1 mostly affects mouth and lips area while HSV-2 most often affects genital regions
- Itching, burning or pain may occur in HSV-1 prior to breakout, but no prominent symptoms in HSV-2 before sore appears
- Type 1 lesions may be crusted blisters, reddish areas or slightly raised areas, whereas lesions in type 2 are crusty or fluid-filled and red in colour
Causes of Herpes
Herpes simplex 1 and herpes simplex 2 are the major causes of herpes.
These viruses are extremely contagious and easily transmitted through direct contact.
Herpes simplex virus 1 is spread by contact like sharing utensils or kissing, making it difficult to pin point the source of virus acquisition.
People of all ages can acquire HSV-1 infection due to its easy transmission mode.
At present, a number of genital sores cases are caused by HSV-1, which is spread by oral sex.
HSV-2 is typically transmitted sexually, so those involve in sex with affected individuals are at high risk.
HSV-2 is not that common; however most people having this virus are unaware and potentially pass it down to others.
The virus can traverse a break in skin during anal, oral or vaginal sex.
The herpes virus can go into the moist membranes of anus, cervix, urinary opening, vagina or penis.
It contaminates the healthy cells upon entering the body, causing swelling, blisters and sores.
In addition to sex organs, fingers, lips, gums, eyes, mouth, tongue and other body parts can also get affected by genital herpes.

HSV-2 can be transmitted by pregnant women to babies at time of birth.
The maximum transmission risk during childbirth is for those women who got infected with herpes virus during pregnancy.
There also exists a close relation between the functioning of body immune system and outbreak of herpes.
Individuals having suppressed immune systems, due to medications, infection, stress or any other reason, are vulnerable to longer-lasting and more frequent outbreaks.
Signs and Symptoms
No symptoms are experienced by most of the people for months or even years after getting infected with herpes virus.
The ones who do have initial period symptoms usually notice them around four days (average range is between 2 to 12 days) after getting exposed to virus.
A group of pus-filled bumps or painful blisters are developed around the infected region.
As these fluid-filled lesions are burst very easily, so they might never come into notice, rather people observe painful small ulcers or red sores.
For primary infection, these lesions typically last for 2 to 6 weeks and 5 to 10 days in case of recurrent infection.
A scab is eventually developed over each sore, which falls off and leaves a reddish area that gets faded with time.
The most common areas for herpes type-2 infection in men are anus, buttocks, upper thighs, scrotum and penis.
In women, anus, cervix, vagina and external genitalia are mostly infected.
Particular genital herpes symptoms in women include small pus-filled blisters (vesicles) on vaginal opening and vulva, also known as vaginal herpes.
The rupturing of vesicles results in painful ulcers. Most of the females experience inflammation of cervix, known as cervicitis.
In some women, the only indication of genital herpes can be cervicitis.
Women having genital herpes may experience pain during urination with inflammation and infection of urethra.
Symptoms of Primary Infection
The term primary infection is used for occurrence of herpes, when an individual is infected for first time.
These symptoms can be extremely severe including vaginal discharge, pain while urinating, itching and pain, red blisters on skin, tender and inflated lymph nodes, cold sores around mouth, malaise (feeling low or unwell), high degree fever and ulceration or blisters on cervix, in the vagina or on external genitalia.
Symptoms of Recurrent Infection
In case of recurrent infection, the symptoms are less severe and last for less time in comparison to symptoms of primary stage infection.
Symptoms will usually not last for more than ten days.
These include red blisters, cold sores around mouth, ulceration or blisters on cervix and pain, tingling or burning in area of outbreak around 24 hours prior to any visible indications (known as prodromal phase of infection).
Eventually, recurrences are much less severe and happen less often.
Diagnosis
HSV-1 lesions are mostly identified by patients themselves or near ones, due to the look and location of cold sores.
Doctors can then make diagnosis on the basis of same symptoms and indications.
HSV-2 can also be recognized by appearance, but, most of the people do not experience any noticeable symptoms, requiring the need of tests to make diagnosis.
HSV-1 and HSV-2 are diagnosed and distinguished by few tests including viral cultures, blood test for virus and antibody test.
Treatments
The treatment of both oral herpes and genital herpes is aimed at relieving the pain and preventing multiplication of virus.
Treatment of Cold Sores
The untreated cold sores typically disappear in 7-10 days time.
Either oral or topical antiviral medications are used for treatment of cold sores.
Primary infections are mostly treated using oral antiviral, but topical antiviral medications are mostly used for treating recurrent infections.
Topical medications are generally not considered as effective for cold sore treatment, in case of severe symptoms.
Treatment of Genital Herpes
Antiviral therapy is used for treatment of genital herpes and is recommended for patients experiencing recurrent herpes or first outbreak.
Treatment at very first outbreak may help in providing some relief.
Generally, treatment is started within 5 days of initiation of first outbreak, when new sores and blisters are still forming.
There are three phases of treatment of genital herpes:
Initial treatment
In case of presence of visible symptoms like sores, when the patient is first diagnosed with genital herpes, the doctors prescribe a short course of antiviral therapy of typically 7-10 days, for relieving or preventing the sores from getting worse.
The doctors may move to next step of treatment if sores are not healed in time.
Intermittent treatment
Doctors typically recommend an antiviral medicine for the patient to keep on hand if another sore breaks out, known as intermittent therapy.
One can take medicines for 2-5 days immediately at noticing sores or feeling its eruption.
The immediate medication will help in reducing the duration and severity of symptoms.
Suppressive treatment
For recurrent outbreaks, one may think about taking an antiviral medicine on daily basis, called as suppressive therapy.
Those having more than 6 outbreaks annually can experience a 70% – 80% reduction in number of outbreaks due to suppressive therapy.
Most of the people taking regular antiviral drugs do not have outbreaks at all.
We have created special kit for those who want to boost their immune system. This kit could help to prevent herpes outbreaks as well.
Some important points to consider regarding treatment are:
- The outbreak of herpes can be treated safely during pregnancy
- As virus is the cause of herpes so antibiotics will not be helpful in treating herpes
- Treatment for oral herpes is not appropriate for genital ones.
- Timely medication can cut down the span of an outbreak and aid in reducing discomfort.
Natural ways to fight herpes
There are some things one can do at own for reducing the pain of genital herpes or cold sore, and to prevent worsening of the lesions and spreading/recurring of infections.
- Apply cold compresses:
Place an insulated ice-pack on lesions for as long as it makes one feel better.
This will help in lessening the pain.
- Do not scratch:
One must avoid scratching and touching lesions caused by herpes, as it can result in the spreading of infection to other areas of skin.
- Keep the sores clean:
Genital herpes and cold sore infections can become infected with bacteria from patient’s hands or, from feces or urine in the former case.
It is essential to keep the area of blisters and sores dry and clean for avoiding an additional infection. As well regularly wash hands.
- Reduce stress:
Stress can interfere with the best possible functioning of immune system.
Reducing stress may help in prevention of excessive recurrences of herpes.
- People having this virus should try to avoid direct contact with other to protect them from getting infected.
- Strengthen immune system by taking balanced food, vitamins, doing sport and live healthy.
A number of herbal remedies are also considered effective and clinically useful for treating herpes simplex.
Most researched antiviral herbs include lemon balm, sage, peppermint, rosemary and wild thyme.
An absolute treatment of a patient having HSV needs use of such herbs that interfere directly with virus and the ones that offer support to the immune system.
Latest Researches/ Theories on Herpes
Researchers are working hard on novel ways for fighting herpes.
Microbicides, chemicals offering protection against infection by killing virus and bacteria before going into body, is one option being explored for new treatments of genital herpes.

Basidial fungi have been known for long as a source of antitumor compounds.
Latest research has presented data regarding the antiviral functions of higher basidial fungi against herpes.
A new antiviral class is under research and development process, known as helicase primase inhibitors, for inhibiting the replication of virus.
A famous company Genocea is using herpes protein, referred as ICP4, together with an antigen that incites an antibody response, for the development of a therapeutic vaccine for herpes.

They expect to make it accessible for patients by 2020.
Some scientists are using CRISPR/Cas9, a gene editing tool, for targeting and cutting particular sections of DNA.
Their main target is the complete elimination of herpes virus.
How to live with herpes?
It can be quite tough to find out about having herpes, but it is a very common infection and certainly not the end of the world.
Although, the virus does hang around in body for life-time, but that does not mean that one will be having sores all the time.
There are medications and treatments for relieving the symptoms, reducing frequency of outbreaks and making the transmission of virus less likely.
The best thing one can do is to follow the doctor’s directions completely.
Moreover, one can also seek assistance from the online support groups for ones having herpes.